The processor (the ‘brain’ of a device)
Computers are everywhere, and so is computation. If you know where to look, the effects of computerisation can be seen in non-digital objects.
A
Agile
An approach to software development, originally defined in the Agile Manifesto. It focuses on iteration, steady growth and responding to change, rather than trying to plan everything up front.
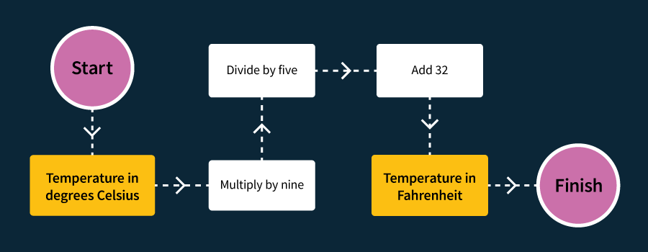
Algorithm
A repeatable, unambiguous set of instructions to perform a task or computation.
B
BASIC
Beginners’ All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code. A coding language designed at Dartmouth College, USA in the 1960s. For many decades it was an introduction to programming for beginners.
Blockly
A visual programming system made by Google that runs inside your web browser.
Blockly Maze
One of the games available on Blockly where users steer a character around a maze.
Blockly Turtle
One of the games available on Blockly where users make line drawings.
Bug
A mistake in a program. Minor bugs may cause it to behave incorrectly; major bugs may stop it working entirely.
C
Checksum
A number that can be calculated using arithmetic to confirm the validity of some data.
Compiler
A program that converts source code into executable code.
CPU
Central Processing Unit which is the main computational processor of a computer.
E
ENIAC
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the world’s first general purpose electronic computer. That means it was not fixed doing one task, but could be ‘reprogrammed’ in order to change what it did. Reprogramming it involved rewiring and connecting its electronic parts. It was mainly used to generate tables of numbers used by the US Army for firing artillery guns.
End-user
The person who will use the end-product or need the answer to the problem.
F
Function
An instruction or command in a programming language
I
Interpreter
A program that transforms source code to executable code a line at a time, running it as it goes.
L
Logic
A formal set of rules that can be followed to make a clear decision. Algorithms at the heart of a computer program are usually built around logical rules.
M
Machine Code
Code that the processor of a computer can run directly; not usually written by hand these days.
Microcontroller
A tiny computer on a single chip, often found in computer electronics.
O
Operating System
The ‘base layer’ of a computer or smartphone. The operating system provides access to core hardware and software features (such as disk storage or networking). Computer programs run on the top of the operating system, and talk to it to integrate with those features, rather than having to talk to them all directly.
P
Pair programming
Two programmers working together at one computer to write code.
Processor
The circuitry in a computer that performs the instructions from a computer program; these days, a small chip.
Program
A set of instructions that can be given to a computer for it to perform a task.
Programming Language
What computer programs are written in. They must be interpreted or compiled in order to run.
S
Scrum master
A member of an agile team responsible for managing the team’s process.
Source Code
The code of a program, written in a programming language.
Sprint
Repeating period of time spent working.
U
UNIX
Uniplexed Information and Computer Systems. An operating system for computers. Originally developed in the 1970s, forms of Unix are still used on computers today. The two most notable Unix-based operating systems today are MacOS, used by every Apple computer, and Linux, most commonly found on servers across the internet.
No comments:
Post a Comment